Which Does Not Belong to the Peripheral Nervous System? Unraveling the Body’s Intricate Wiring

Image: delightsand.weebly.com
Among the various components of the nervous system, the autonomic nervous system (ANS) stands out. As its name suggests, the ANS operates largely independent of conscious control, regulating vital bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing. It acts as an invisible puppeteer, orchestrating these processes without our conscious awareness.
However, despite its close connection to the PNS, the ANS possesses a unique characteristic that sets it apart: it operates without the direct involvement of the CNS. The ANS has its own dedicated circuits and control mechanisms within the body, enabling it to function autonomously.
Understanding the Difference: CNS, PNS, and ANS
To fully grasp the distinction between the CNS, PNS, and ANS, it’s crucial to delve into their fundamental differences:
- CNS: The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord, serving as the central hub for processing sensory information and coordinating motor responses.
- PNS: The peripheral nervous system encompasses all the nerves that extend from the CNS to the rest of the body, including sensory nerves, motor nerves, and autonomic nerves.
- ANS: The autonomic nervous system is a specialized branch of the PNS, responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions. Unlike other parts of the PNS, the ANS operates independently of the CNS.
Challenging the Classification: ANS as a Separate Entity
Given the ANS’s distinct characteristics, some neurologists argue that it should be considered a separate entity from the PNS. First, the ANS functions autonomously, relying on its own control mechanisms rather than direct input from the CNS. Second, its unique structure, involving ganglia and plexuses, sets it apart from other components of the PNS.
Moreover, research has uncovered significant differences in the development, neurochemistry, and disease associations of the ANS compared to the PNS, further strengthening the case for its independent classification.
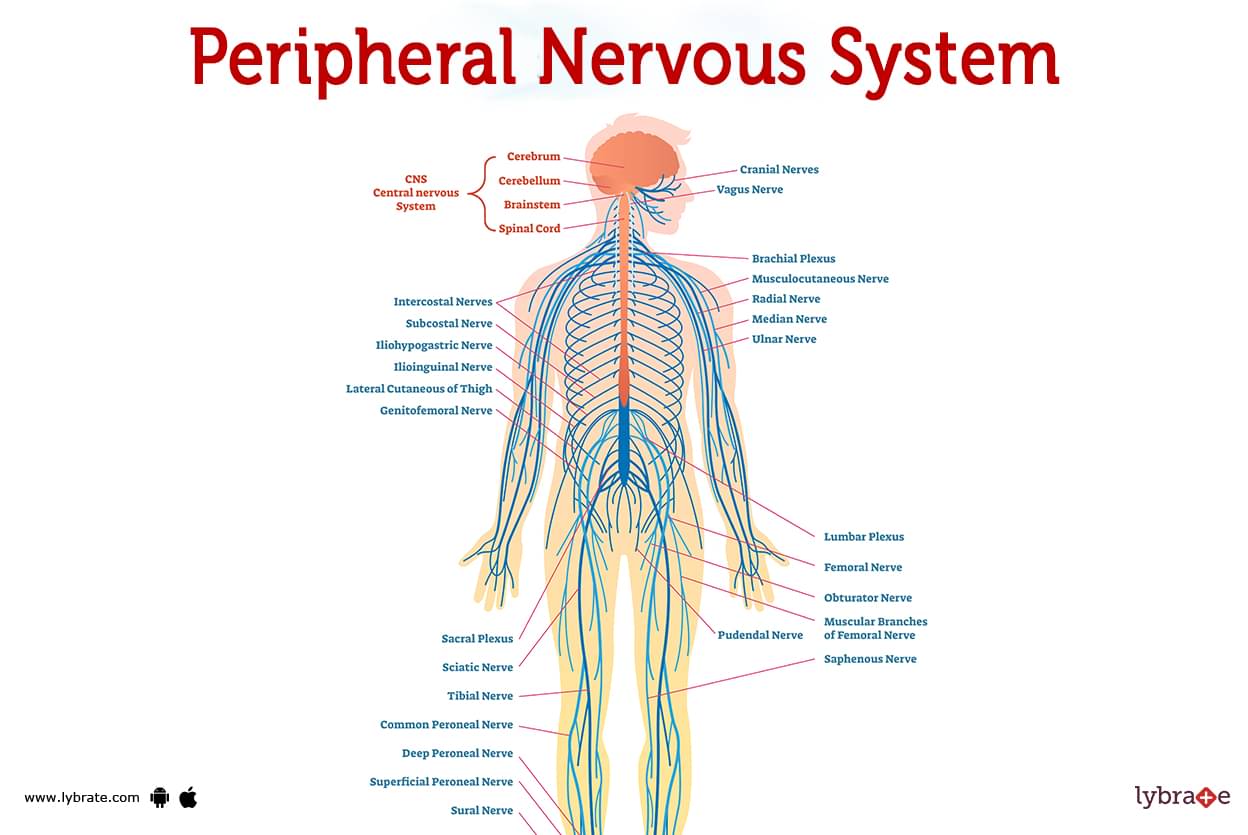
Image: ar.inspiredpencil.com
Which Does Not Belong To The Peripheral Nervous System
Conclusion: Recognizing the Autonomic Nervous System’s Unique Role
The debate over whether the autonomic nervous system belongs to the peripheral nervous system reflects the complexity and interconnectedness of the nervous system. While the ANS collaborates with other components of the PNS, its distinct characteristics and autonomous functions make it a unique and essential player in maintaining the body’s delicate balance.
By unraveling the intricate wiring of our nervous system, we gain a profound appreciation for the intricate symphony it orchestrates within us. Recognizing the distinctive nature of the autonomic nervous system empowers us to understand how our bodies function seamlessly, adapting to changing conditions without conscious effort.
Embrace the marvel of the human body, where even within intricate systems, subtle differences can lead to extraordinary outcomes. Let this exploration of which does not belong inspire a deeper understanding of our physical selves and motivate us to cherish the delicate dance of life.
